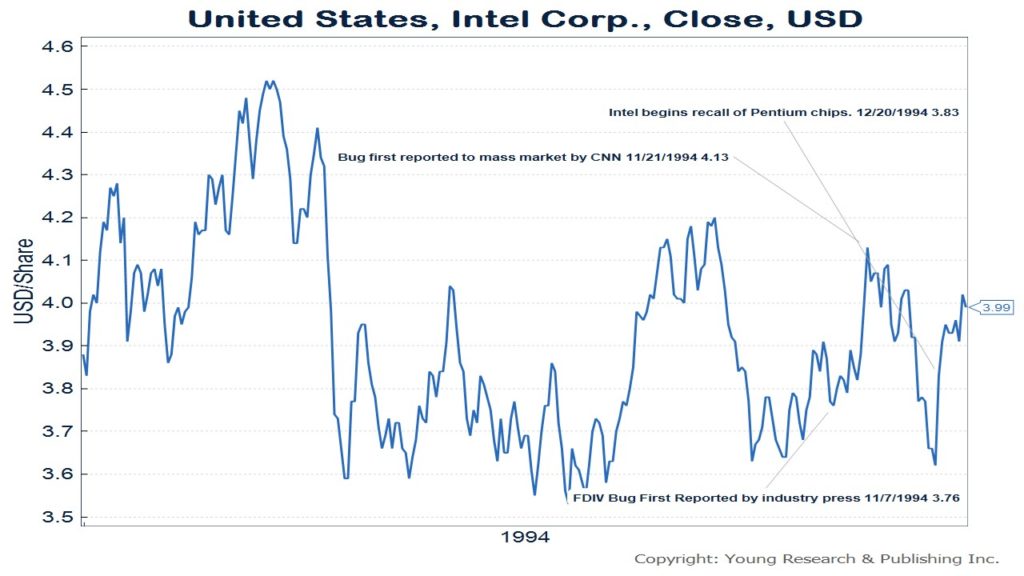
History has a way of repeating itself. In early 1995 I wrote about a math professor named Tom Nicely, who worked at Lynchburg College. Nicely was examining prime numbers using a group of five personal computers. While four of the computers gave Nicely the correct answer to a problem, 1.2126596294086, the fifth turned up a slightly different answer, 1.212659624891157804.
The cause of the fifth computer’s error was the Intel Pentium processor installed on it. Nicely called Intel to explain, but was given the cold shoulder. Next, he did something which at that point was still novel, he asked for help on the Internet. Others checked Nicely’s work and came back with the same results, confirming his conclusions.
Intel had already known about the problem since May when one of their own researchers had discovered it, but only after they had been backed into a corner by independent confirmation did Intel acknowledge Nicely’s research. The company even offered him a consulting job.
The bug was first reported in an industry journal known as Electronic Engineering Times, but when it was reported by the mass media on CNN on November 21, 1994, the stock dropped over 12.3% in a little less than a month. The stock only began gaining again after Intel offered a recall on December 20th.
Here We Go Again
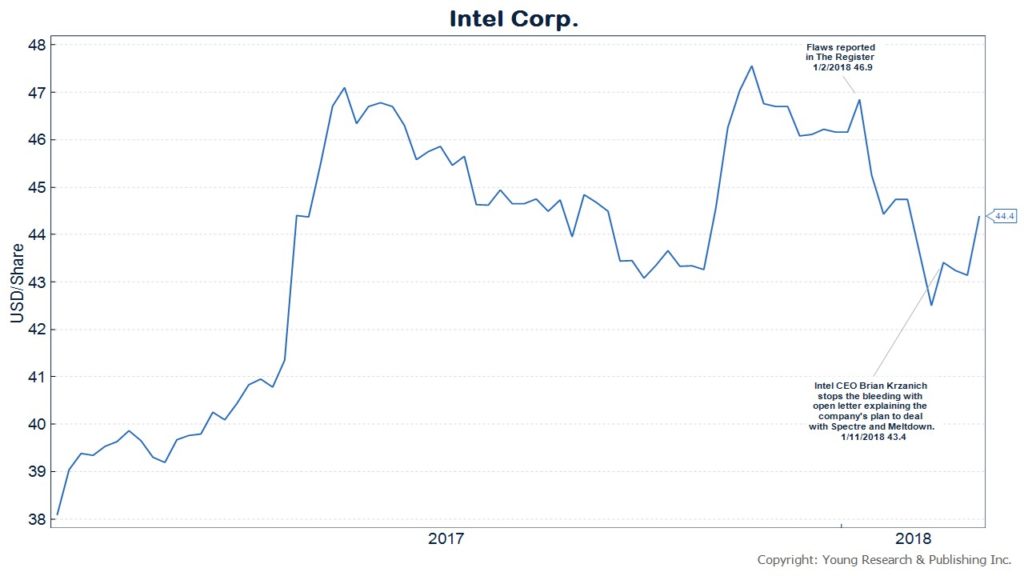
Today Intel is in a somewhat similar, though not exact, position. A group of researchers connected by the Internet, have exposed a much larger flaw in Intel’s processors, and now the company needs to deal with the fallout.
The issues, known as Spectre and Meltdown, could potentially be used by hackers to attack computers using Intel processors. The news was again first reported in an industry journal, the Register, out of the U.K. But in today’s rapid information world, it didn’t take much time to disseminate to the market. Intel’s share price dropped over 9.2% in eight days.
Only after CEO Brian Krzanich wrote an open letter to the tech industry explaining Intel’s next steps were investors willing to climb aboard Intel once more.
Do You Have a Game Plan?
I do not relay this story to you to shame Intel. What I want you to see here, is that companies often undergo rough periods. The tech industry in particular is prone to volatility thanks to complex products and low barriers to entry. The unexpected happens, and without a game plan you may see a lot of your own money wiped off the board quickly.
My game plan for decades has been one laid out first by Ben Graham in the Intelligent Investor. Graham wrote, “One of the most persuasive tests of high quality is an uninterrupted record of dividend payments for the last 20 years or more. Indeed, the defensive investor might be justified in limiting his purchases to those meeting this test.” I would add to Graham’s astute analysis that focusing on companies dedicated to increasing dividends helps as well.
What are Your Goals?
Another factor in investing is understanding the business you are investing in. Not many investors today can honestly say they understand what the Spectre and Meltdown flaws in Intel’s chips really are. Are you prepared to invest in a company that builds a product you don’t understand and can’t explain? These shares are no doubt appropriate for some portfolios, but if risk avoidance is one of your goals, understanding the company from top to bottom is a good place to start.
I practice risk avoidance in all aspects of life, and especially in investing. If you are in or nearing retirement and are looking to relieve the burden of the work that must be done to minimize risk in your investment portfolio, I urge you to visit the website of my family run investment advisory, Richard C. Young & Co., Ltd. You can sign up for our client letter, free even for non-clients, to get a better idea of the principles used to make investment decisions.
Originally posted on January 19, 2018.